Sintered Permanent Samarium Cobalt Sm2Co17 Magnets
Min.Order : 5 Pieces Quick Quotation >
Item Details
Product Description
Sintered Permanent Samarium Cobalt Sm2Co17 Magnets
1.Product Introduction of Sintered Permanent Samarium Cobalt Sm2Co17 Magnets
Samarium-cobalt (SmCo) magnets have excellent magnetic properties, with a maximum energy product of up to 32 MGOe, a low temperature coefficient and high stability. They are also highly resistant to oxidation and require no coating under normal conditions.
The BHmax value ranges from 16 to 32 MGOe. Magnetic assemblies constructed with samarium cobalt can therefore be considerably reduced in volume.They are more expensive and weaker than neodymium magnets, but they have a higher Curie temperature making them suitable for use in extreme temperatures.
2.Product Parameter(Specification)of Sintered Permanent Samarium Cobalt Sm2Co17 Magnets
|
Material |
SmCo |
|
Advantages |
1. Resistant to temperatures above 300° C, so they remain stable at temperatures far above the Curie point of materials; 2. Corrosion-resistant; |
|
Technology |
Sintered |
|
Magnet Shape |
U shape, Disc, Cylinder, Block, Ring and other customized shapes |
|
Technical details |
1. Density: 8304 kg/m³ ((0.300 lbs./in³); 2. Magnetic field required for saturation: ±50 kOe; 3. BHmax value: 151-247 kJ/m³. |
|
Applications |
1. Medical implants and prostheses; 2. Sensors; 3. High-temperature pumps, motors 4. Turbomachinery. |
3.Samarium Cobalt permanent magnets – table
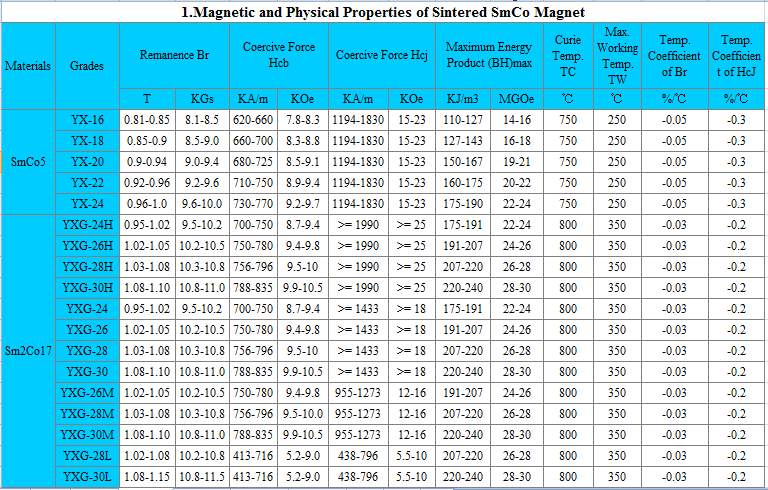
4.Packing and shipping of Sintered Permanent Samarium Cobalt Sm2Co17 Magnets


1.Q:Will magnets lose their power over time?
A:Do lose a very small fraction of their magnetism over time. For example, SmCO magnet has been shown to be less that 1% over a period of ten years.
2.Q:Can a magnet that has lost its magnetism be re-magnetized?
A:If the magnet has not been damaged by extreme heat, it can be re-magnetized back to its original strength.
3.Q:What are the standard industry definitions of "North" and "South" Pole?
A:The North Pole is defined as the pole of a magnet that, when free to rotate, seeks the North Pole of the earth. Similarly, the South Pole of a magnet seeks the South Pole of the earth.
4.Q:Can a particular pole be identified?
A:Yes, the North or South Pole of a magnet can be marked if specified.
5.Q:What does "orientation direction" mean?
A:Magnets have a “grain” in that they can be magnetized for maximum effect only through one direction.
6.Q:Why are most neodymium plated or coated?
A:Neodymium magnets are mainly constructed of Neodymium, Iron and Boron. Iron can oxidize very easily when exposed to moisture and will rust over time.
Payment & Shipping

More Product
Recommend Product